The OKR cycle simply explained – 5 minutes reading time
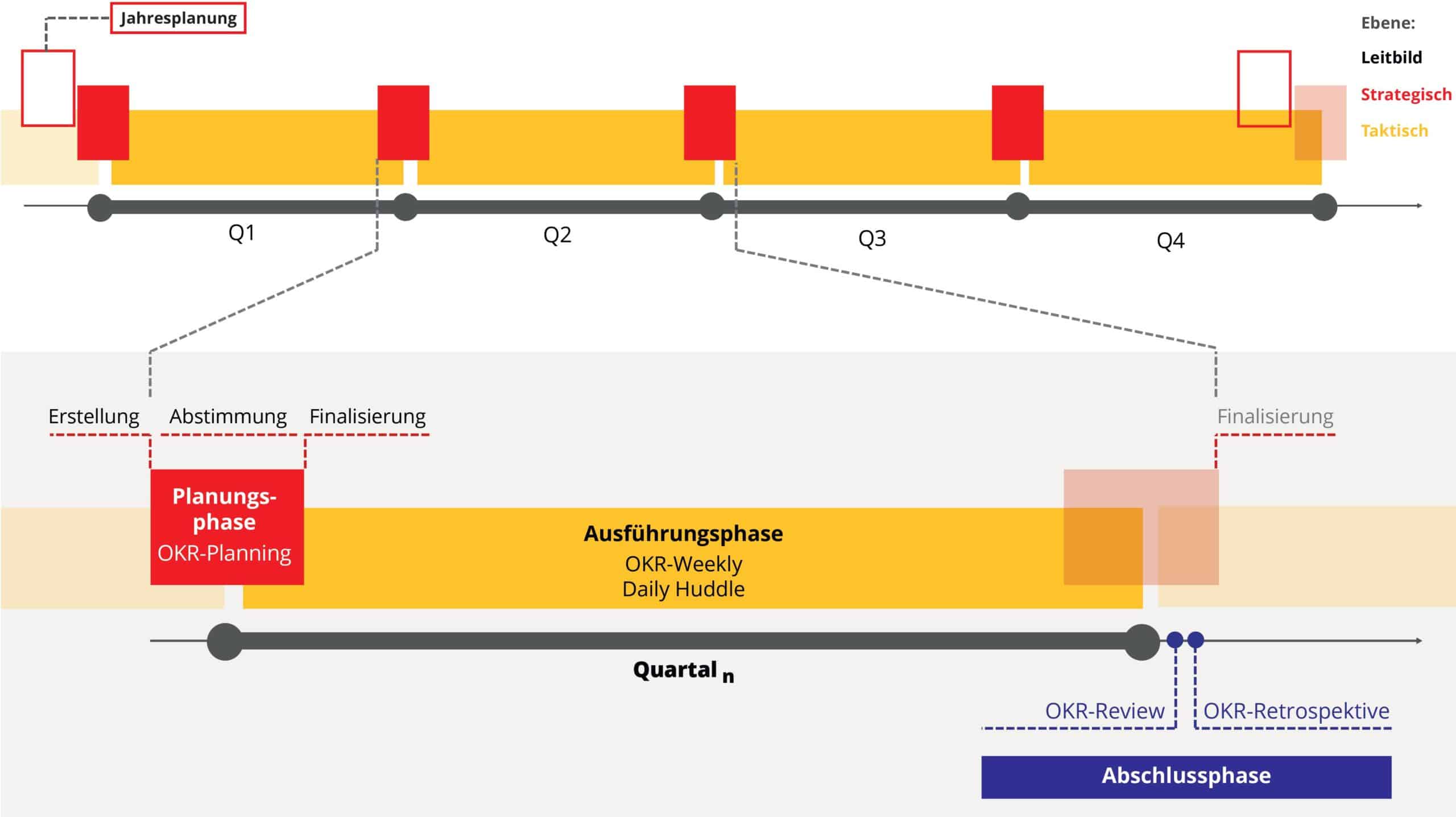
The OKR cycle consists of three main phases: Planning Phase, Execution Phase and Completion Phase. After the final phase, it is iterated over and over again.
The duration of a cycle or cadence can vary between two and four, maximum six months. We work with most companies with a cadence of three months.
The 3 phases of the OKR cycle
The OKR method helps to implement the company’s vision in iterative cycles if it is used correctly.
- Planning phase – planning and coordination: OKR helps to plan the implementation of the vision and strategy and coordinates measures at all levels, departments and teams.
- Execution phase – execution and progress: The OKR method supports the implementation of focused measures. It is important that progress is continuously measured, evaluated and, if necessary, discussed.
- Final phase – review and adapt: All teams review the progress of a cycle based on data and facts and learn from successes and mistakes – both in terms of content and methodology.
At this point, we will first briefly introduce you to the various phases:
The planning phase at the beginning of the OKR cycle
The cycle logically begins at the start of the OKR cycle, more precisely shortly before the start of the OKR cycle with the planning phase. The OKR sets are created in the OKR planning as part of the planning phase.
At company level, the management or the management team is responsible. The OKR sets of the department and the respective teams are then created – the targets are cascaded downwards, i.e.“top down”.
Departments and teams also coordinate – horizontally.
In addition, teams can propose OKR sets to the head of department and the management or leadership team (“bottom up”). In this way, the OKR method enables all levels of the company to meet regularly to discuss whether they are successful and how they measure this success.
The OKR cycle and the execution phase
In the execution phase of the OKR cycle, work is carried out to achieve the objectives and progress is measured and monitored – similar to a sprint in Scrum.
There are daily and weekly check-in meetings. The daily stand-up meeting is called the Daily Huddle. The weekly meeting is called OKR-Weekly. During the execution phase, exceptional OKR planning can also be carried out and new OKR sets can be created – but only in the event of a completely unexpected event, such as 9/11 or Covid-19.
The final phase rounds off the OKR cycle
At the end of the completed OKR cycle, the OKR sets are measured and evaluated and assessed in the final OKR review. In addition, the OKR process is methodically evaluated and optimized in the OKR retrospective (“inspect and adapt”).
On the pulse of time – the OKR Heartbeat. Because of the fixed rhythm created by the cadence of the OKR cycle, we call this “OKR heartbeat”. The cyclical cycle can be clearly seen in the diagram of the OKR cycle.
The figure illustrates the exact timing even better – here is a 3-month OKR cycle as an example. We call this illustration the OKR heartbeat because it shows exactly one pulse beat in a linear fashion.
The OKR Cycle – Dos and Don’ts
Dos
- Experience has shown that a cadence of three months is advisable at the beginning. Later, we will examine whether it makes sense to reduce the cadence to two months – or increase it to four months. The duration of the OKR cycle varies depending on the sector and the company’s general conditions.
- Make sure that objectives and key results are achievable within an OKR cycle. If the objectives and key results require a longer period of time, you need to break them down into smaller units – so that they can be achieved within a cycle.
- Ideally, you should first introduce the OKR method at company level in the management team. In the next OKR cycle at department level, then again one cycle later at sub-department level and finally at team level. It may also make sense to start in a pilot team or a pilot department.
- The top-level OKR sets are communicated to the company two to three weeks before the start of the new OKR cycle. This triggers the OKR planning process throughout the company.
- This process usually extends into the OKR cycle. It takes time for it to be finally agreed, negotiated, concluded and fully documented. An OKR template is sufficient for small companies, but OKR software is more suitable for larger companies.
- Shortly after the end of an OKR cycle, it is important to reflect on how the OKR process can be methodically optimized. Corresponding actions are derived from this. This applies to the individual teams and the entire company at regular intervals.
- The tasks (tasks for key results) can change during the OKR cycle – no, they even have to be changed if you realize that the measures are pointless.
Don’ts
- OKR sets should not be carried over from one OKR cycle to the next (so-called “evergreens”), which is in the nature of operational activities (“business as usual”). OKR sets should focus on their respective OKR cycles.
- Also bear in mind that the first OKR cycle may not run entirely smoothly. The introduction of the OKR method is neither trivial nor a sure-fire success. Don’t be under the illusion that everything works perfectly, and don’t hesitate to wait too long to get started – just get started! Our OKR experts will be happy to support you.
- Here, too, it is important that you report regularly and transparently on the success (and failure) of the OKR method, for example in town hall or all-hands meetings or via the intranet – and learn from this. Do not ignore the resistance.
We support you in the introduction of OKR, in OKR training and in optimizing the use of OKR in your company.